Serena Zone
Overview
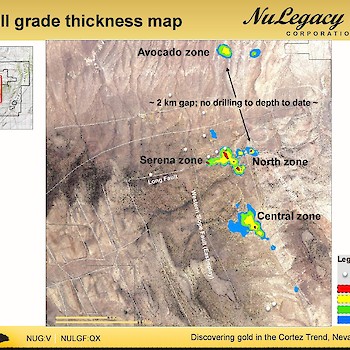
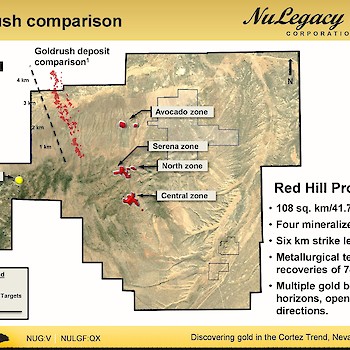
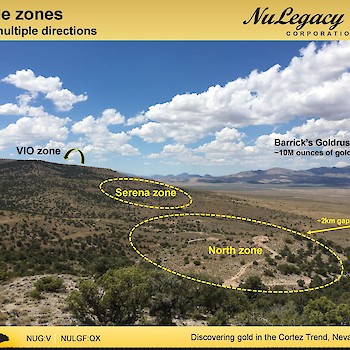
The Serena Zone is NuLegacy’s most recent discovery of Carlin-type mineralization on the Red Hill property. The discovery of Serena represents another successful application of combining geophysical and geochemical data with bold step-outs from known mineralization. The success of our exploration approach at Serena has validated our exploration model and created the basis for pursuing similar targets elsewhere in the district.
Geology
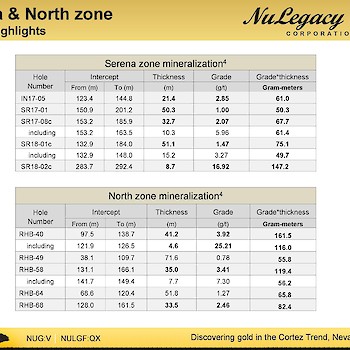
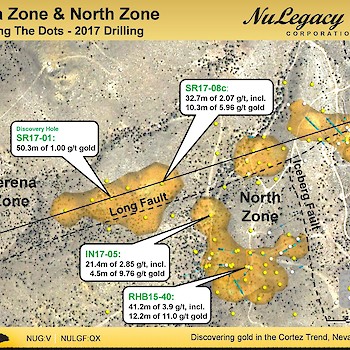
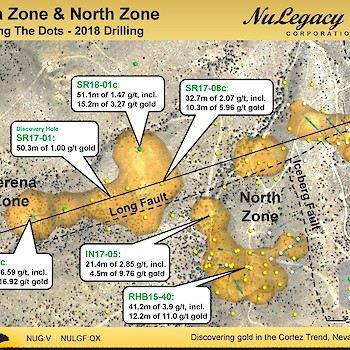
The stratigraphy of the Serena Zone consists of a ~100-200 m thick package of Tertiary volcanics, sediments, and tuffaceous volcaniclastics. These Tertiary rocks unconformably overlie the silty Devonian carbonates of the Horse Canyon Formation, which overlie the more massive carbonates of the Devonian Wenban Formation. The Serena Zone is understood to exist at the structural intersection of the Long Fault, also associated with mineralization in NuLegacy’s North Iceberg Deposit, and the West Iceberg fault, which was identified in a CSAMT geophysical study in early 2017. The Carlin-type mineralization in the Serena Zone is associated with fine-grained pyrite and is hosted in silicified breccias and jasperoids at the base of the Horse Canyon at the Horse Canyon-Wenban contact.